Managing payroll as a small business owner involves more than just issuing paychecks. Ensuring compliance with tax regulations is crucial to avoid penalties and maintain smooth business operations. One essential tax form you need to be aware of is Form 941, also known as the Employer’s Quarterly Federal Tax Return.
If you’re unsure about what Form 941 is, who needs to file it, and how to do so correctly, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know.
What Is Form 941?

Form 941 is the IRS tax form used by employers to report the federal payroll taxes they withhold from employees’ wages. Specifically, it covers:
- Employee wages and compensation paid during the quarter.
- Federal income tax withheld from employee paychecks.
- Social Security and Medicare taxes (FICA taxes) owed by both the employer and employee.
- Adjustments for sick pay, tips, and overpayments (if applicable).
Form 941 ensures that the IRS receives timely reports on payroll tax liabilities and that businesses comply with tax obligations.
Who Needs to File Form 941?
Most businesses that pay employees and withhold payroll taxes are required to file Form 941. This includes:
- Small businesses with employees
- Corporations, LLCs, and sole proprietors with payroll
- Nonprofits and tax-exempt organizations with paid staff
- Seasonal businesses (though they may not file every quarter)
Who Is Exempt from Filing Form 941?
Some employers do not need to file Form 941, including:
- Businesses that file Form 944 instead: Small businesses with minimal payroll tax liability ($1,000 or less per year) may be eligible to file Form 944 (Annual Federal Tax Return) instead of Form 941.
- Household employers: If you hire household employees like a nanny or caretaker, you report their wages on Schedule H instead of Form 941.
- Agricultural employers: Businesses that employ farm workers report payroll taxes on Form 943 rather than Form 941.
If you’re unsure about whether you need to file Form 941, consulting a payroll service provider can help ensure compliance.
When Is Form 941 Due?
Since Form 941 is filed quarterly, you must submit it four times a year. The IRS deadlines are:
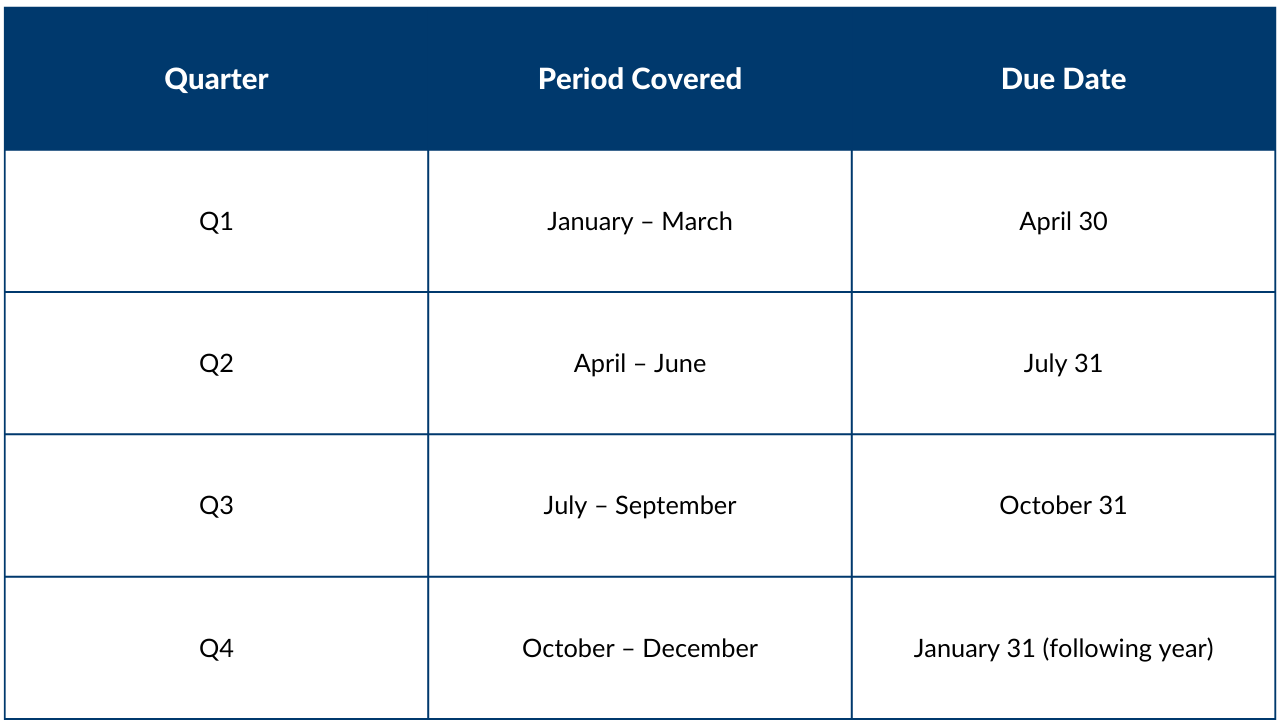
Happens if You Miss the Deadline?
Failing to file Form 941 on time can lead to IRS late filing penalties:
- 5% of the unpaid tax per month, up to 25% maximum.
- If you file but don’t pay the taxes, an additional penalty of 2% to 15% applies based on the delay.
- Interest charges accrue on unpaid balances.
How to Fill Out Form 941
Form 941 includes multiple sections where businesses report payroll and tax information. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
1. Employer Information
- Business name, EIN (Employer Identification Number), and address
- Indicate the correct quarter you are filing for
2. Wages and Tax Withholding
- Total wages, tips, and compensation paid to employees
- Federal income tax withheld from paychecks
- Social Security and Medicare taxes (employer and employee portions)
3. Adjustments
- Report any tax adjustments due to sick pay, tips, group-term life insurance, or overpayments.
4. Payment and Deposits
- Report the total tax liability and deposits made throughout the quarter.
- If there’s an outstanding balance, you may need to submit a payment.
5. Signature and Filing Method
- Sign the form and choose electronic filing or mail submission.
How to File Form 941

There are two main ways to file Form 941 with the IRS:
1. Electronic Filing (Recommended)
- Faster processing and confirmation
- Reduces the chance of errors
- Can be done using IRS-approved payroll providers like guHRoo
2. Paper Filing
If you prefer mailing the form, send it to the appropriate IRS address based on your location and whether you’re including a payment.
Common Filing Mistakes (and How to Avoid Them)
Mistakes in Form 941 filings can lead to penalties. Here are the most common errors and how to avoid them:
- Misreporting Wages – Double-check payroll records to ensure accuracy.
- Incorrect Tax Calculations – Use IRS tax tables or an automated payroll system.
- Missed Deadlines – Set reminders or automate filings to avoid penalties.
- Filing the Wrong Form – Verify if you should file Form 941 or Form 944.
- Missing Signatures – Ensure the form is signed and dated before submission.
How guHRoo Simplifies Payroll Tax Filing
Managing payroll taxes can be time-consuming, but guHRoo streamlines the process:
- Automated Quarterly Filings – Avoid missed deadlines and costly penalties.
- Accurate Tax Calculations – Ensures compliance with IRS requirements.
- Integrated Payroll, HR, and Benefits – A complete solution for small businesses.
- Expert Support – Guidance to navigate payroll tax laws with confidence.
Conclusion
Filing Form 941 correctly and on time is a key responsibility for small business owners, but managing payroll taxes can be complex and time-consuming. Partnering with a Professional Employer Organization (PEO) like guHRoo ensures compliance without the administrative burden.
With guHRoo’s PEO services, businesses gain a trusted payroll partner that handles Form 941 filings, payroll tax compliance, HR management, and employee benefits—all in one streamlined solution. By outsourcing these essential functions, small businesses can reduce risk, improve efficiency, and focus on growth.
Discover how guHRoo’s PEO services can simplify payroll, HR, and tax compliance for your business. Contact guHRoo today.





